Space

Mar 5th, 2026 - Follow Earth on Google NASA has confirmed that an interstellar comet brightened dramatically after passing the Sun and released a fresh surge of water vapor and carbon-rich molecules. That delayed outburst exposes material sealed for billions of years in deep freeze between stars and now briefly available for direct study. What SPHEREx saw During a December 2025 observing run, a NASA space telescope called SPHEREx , designed to map the sky in infrared light, recorded the comet's glow in fine ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Mar 5th, 2026 - 'Conan the Bacterium' could really conquer the solar system, new study suggests Chalk up another victory for "Conan the Bacterium"—a rugged germ that fresh research suggests could conquer the solar system. Better known as Deinococcus radiodurans, this microbe is arguably the toughest organism known to science . Past studies have shown it can endure extreme cold, intense radiation, harsh chemicals and profound dehydration—all evolutionary adaptations, perhaps, to what's thought to be ... [Read More]
Source: scientificamerican.com

Mar 5th, 2026 - In April 1978, Voyager 1 was 165 million miles from Jupiter – but that was near enough to begin observations of the gas giant. In the first few months, observations suggested a much more turbulent atmosphere than had been expected based on the earlier Pioneer missions. By January of 1979, Voyager began taking a photo every 96 seconds, creating a timelapse series. Closest approach came March 5, 1979, one day after Voyager 1 had captured photographic evidence of a ring system around the ... [Read More]
Source: astronomy.com
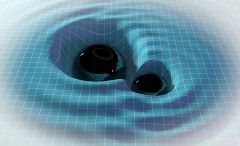
Mar 5th, 2026 - The universe is filled with a cacophony of colliding black holes When black holes collide, the crash generates ripples in the fabric of spacetime— gravitational waves . These distortions travel far out into the universe, but by the time they reach Earth, they have become faint, making them extremely hard to detect. Thanks to a global network of observatories—called the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), Virgo and the Kamioka Gravitational-Wave Detector ... [Read More]
Source: scientificamerican.com

Mar 5th, 2026 - Reading time 3 minutes When the surface of the Sun exploded with activity in May 2024, Earth was hit by the biggest solar storm in more than two decades . The video shown below—made from images captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory—shows the powerful solar flare and coronal mass ejection that sent an onslaught of charged particles hurtling toward us. But of course, our planet wasn't the only one in the line of fire. A study published today in the journal Nature ... [Read More]
Source: gizmodo.com

Mar 5th, 2026 - Astronomers have a new map to find an alien civilization by looking for stars that appear impossibly cold. While it sounds like the plot of an Andy Weir novel, if an advanced civilization wanted to tap nearly all the power of its star, it could gather energy by putting a giant collection of light-catching structures around the star and just directly harvest the energy. That's the foundation of the " Dyson sphere " idea Freeman Dyson laid out in 1960, though most modern versions imagine a swarm ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com
Mar 4th, 2026 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Facebook X Whatsapp Reddit Pinterest Flipboard Join the conversation Add us as a preferred source on Google Get the Live Science Newsletter Get the world's most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox. By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com

Mar 3rd, 2026 - Follow Earth on Google A nearby galaxy has now yielded a resolved census of 1,285 giant star-forming gas clouds. That tally shows its cold gas does not sit as a smooth disk but gathers into discrete structures that shape how, and how slowly, new stars emerge. Inside the lenticular galaxy NGC 1387, what once appeared to be an orderly reservoir of cold material resolves into hundreds of distinct cloud complexes spread across its disk. A cloud census Working with high-resolution maps from the ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Mar 3rd, 2026 - Reading time 2 minutes A massive star nearing the end of its life has donned a new face, changing color and becoming hotter in a surprisingly short amount of time. The dramatic transformation may be indicative of its impending doom, giving us a rare opportunity to witness a supernova in the making. A team of astronomers has been monitoring a red supergiant star in the Large Magellanic Cloud over the past decade, recording an increase in surface temperatures as it evolved to a yellow hypergiant ... [Read More]
Source: gizmodo.com

Mar 3rd, 2026 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Facebook X Whatsapp Reddit Pinterest Flipboard Join the conversation Add us as a preferred source on Google Get the Live Science Newsletter Get the world's most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox. By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com

Mar 3rd, 2026 - Follow Earth on Google Could a frozen moon hide a boiling ocean under its icy skin? That idea may sound like science fiction, but new research shows it could be real. Many moons that orbit the outer planets look cold and lifeless. Thick ice covers their surfaces. However, deep below that frozen layer, liquid water may exist. Since water is essential for life, scientists see these moons as exciting places to explore. A recent study published in Nature Astronomy takes a closer look at what ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Mar 3rd, 2026 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Facebook X Whatsapp Reddit Pinterest Flipboard Join the conversation Add us as a preferred source on Google Get the Live Science Newsletter Get the world's most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox. By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com

Mar 2nd, 2026 - On March 2, 2004, the Rosetta-Philae spacecraft launched from French Guiana, with the goal of rendezvousing with a comet to learn more about the early solar system. The European Space Agency mission would need 10 years, three gravity assist flybys of Earth , and one gravity assist from Mars to get the spacecraft to its target. But in August 2014, Rosetta successfully slipped into orbit around Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko and, a few months later, deployed the Philae lander to its surface. ... [Read More]
Source: astronomy.com

Mar 2nd, 2026 - Smart underwear measures farts, brain cells play Doom , and AI discovers rules of an ancient game. It's a regrettable reality that there is never enough time to cover all the interesting scientific stories we come across each month. So every month, we highlight a handful of the best stories that nearly slipped through the cracks. February's list includes the revival of a forgotten battery design by Thomas Edison that could be ideal for renewable energy storage; a snap-on device to turn those ... [Read More]
Source: arstechnica.com

Mar 2nd, 2026 - Whether or not galaxies merge depends on how strong the gravitational attraction is between the galaxies and whether the universe's expansion is more powerful than gravity. Gravity affects everything in the universe. The Milky Way Galaxy is gravitationally pulling on NGC 3370, nearly 100 million light-years away. The catch, however, is that the gravitational attraction between the Milky Way and NGC 3370 is so tiny that the universe's expansion can overcome it. Over small scales, the force of ... [Read More]
Source: astronomy.com

Mar 1st, 2026 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Facebook X Whatsapp Reddit Pinterest Flipboard Join the conversation Add us as a preferred source on Google Get the Live Science Newsletter Get the world's most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox. By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com